(!) Since support from Microsoft will end on January 14th, 2020, Windows 7 will be excluded from the recommended environment from December 15th, 2019 on this site. Vì lý do Microsoft kết thúc hỗ trợ cho Windows 7 vào ngày 14/01/2020, Windows 7 sẽ là hệ điều hành không được khuyến khích sử dụng với trang web này từ ngày 15/12/2019.
Search by Category / Brand Tìm theo danh mục, nhãn hiệu
Search by Category Tìm theo danh mục
- [Thông báo] Cập nhật địa chỉ kho tập kết hàng hóa tại khu vực miền Nam của MISUMI Việt Nam. Xem chi tiết.
[Announcement] Update on warehouse address in the Southern region of MISUIMI Vietnam. See more. - [Cảnh Báo] Thủ Đoạn Lừa Đảo Từ Nhân Viên Giao Hàng – Yêu Cầu Trả Phí Ship. Xem chi tiết.
[Warning] Fraud Calling from Shipper - Asking to Pay Shipping Fee. See more.
Photoelectric Sensors(Detection Distance:100~7000)
Brand |
|
|---|---|
| CAD |
|
| Days to Ship |
|
1 itemsMặt hàng
- Sort By
-
You can add up to 6 items per a category to the compare list.

BW Series Area Sensor (Universal)
AUTONICS
- Volume Discount
Detection Distance(mm) Type Detection Type Light Axis Arrangement Type Head Shape Detection Light Type Detection Object Amplifier Installation Type Detection Light Color Head Material Detection distance 【classification】(mm) Operating Environment Protection Structure Amplifier Function (Selectable only when Amplifier is installed) Fiber Type (Selectable only when Amplifier is not installed) Fiber clothing material 100~7000 Photoelectric Sensor Transparent Emitting and Receiving Sections Separated Square Multi-Row Colored Surface - Infrared Aluminum - Standard IP65 - - - From: 4,498,304 VND Days to Ship: Số ngày giao hàng: 5 Day(s) or more  5 Day(s) or more
5 Day(s) or more
| BrandNhãn hiệu |
|---|
| Product SeriesDòng sản phẩm |
| From |
| Days to ShipSố ngày giao hàng |
| Detection Distance(mm) |
| Type |
| Detection Type |
| Light Axis Arrangement Type |
| Head Shape |
| Detection Light Type |
| Detection Object |
| Amplifier Installation Type |
| Detection Light Color |
| Head Material |
| Detection distance 【classification】(mm) |
| Operating Environment |
| Protection Structure |
| Amplifier Function (Selectable only when Amplifier is installed) |
| Fiber Type (Selectable only when Amplifier is not installed) |
| Fiber clothing material |
You can add up to 6 items per a category to the compare list. | |
| BrandNhãn hiệu | AUTONICS |
| Product SeriesDòng sản phẩm | |
| From | 4,498,304 VND |
| Days to ShipSố ngày giao hàng | 5 Day(s) or more |
| Detection Distance(mm) | 100~7000 |
| Type | Photoelectric Sensor |
| Detection Type | Transparent |
| Light Axis Arrangement Type | Emitting and Receiving Sections Separated |
| Head Shape | Square |
| Detection Light Type | Multi-Row |
| Detection Object | Colored Surface |
| Amplifier Installation Type | - |
| Detection Light Color | Infrared |
| Head Material | Aluminum |
| Detection distance 【classification】(mm) | - |
| Operating Environment | Standard |
| Protection Structure | IP65 |
| Amplifier Function (Selectable only when Amplifier is installed) | - |
| Fiber Type (Selectable only when Amplifier is not installed) | - |
| Fiber clothing material | - |
Loading...Tải…
ConfigureTạo
Specification/DimensionsĐặc điểm kỹ thuật / Kích thướcĐặc điểm kỹ thuật / Kích thước
-
Detection Distance(mm)
- 0-3M
- 0.1-3m
- 0.1-2.5m
- 1~15
- 1~30
- 3~50
- 5~15
- 5~30
- 10-50 (white matte paper 50X50 mm)
- 10~30
- 10~50
- 15m
- 20~100mm
- 30
- 30 (white matte paper 100X100 mm) / 15 (transparent glass 50X50 mm, t=3.0 mm)
- 30~200
- 35~200mm
- 50
- 50~3000
- 100
- 100mm
- 100-3000 (when using Mirror MS-2A) / 100-4000 (when using Mirror MS-2S) / 100-5000 (when using Mirror MS-3S)
- 100 (white matte paper 100X100 mm)
- 100~1000
- 100~2000
- 100~3000
- 100~5000
- 100~7000
- 200
- 200 (white matte paper 200X200 mm)
- 300
- 300mm
- 300 (white matte paper 100X100 mm)
- 500
- 700
- 1000
- 2000
- 2000mm
- 3000
- 4000/20000
- 5000
- 7000
- 10000
- 15000
The detecting distance can vary with your amplifier, operating environment and the detected object.
-
Type
- Photoelectric Sensor
- Laser Sensor
- Fiber Unit
- Fiber Optic Sensor
-
Detection Type
- Transparent
- Reflection
- Liquid Surface Contact
- Recurrent Reflection
-
Light Axis Arrangement Type
- Emitting and Receiving Sections Integrated, Single
- Emitting and Receiving Sections Integrated, Reflection Plate Used
- Emitting and Receiving Sections Separated
- Use a flood and light-receiving integrated unit.
-
Head Shape
-
Cylindrical

-
Square
-
Screw
-
Hex

-
Low Profile

-
Cylindrical
-
Detection Light Type
-
Standard

-
Small Spots
-
Wide

-
Multi-Row
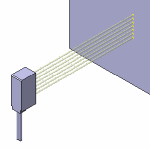
-
Laser
-
Diffused Light

-
Standard
-
Detection Object
- Colored Surface
- Transparent Body
- Small Area
- Thin Line Shape
-
Amplifier Installation Type
- Built-in Type
-
Detection Light Color
-
Head Material
-
Detection distance 【classification】(mm)
- ~10
- ~20
- ~30
- ~50
- ~100
- ~200
- ~300
- ~400
- ~500
- ~1000
- ~2000
- ~3000
- ~4000
- ~5000
- ~10000
- More than 10000
* ~20 represents over 10, and 20 or less.
-
Operating Environment
-
Protection Structure
-
Amplifier Function (Selectable only when Amplifier is installed)
-
Fiber Type (Selectable only when Amplifier is not installed)
-
Fiber clothing material
Application example related to this categoryVí dụ ứng dụng liên quan đến danh mục này
Related Categories to Photoelectric SensorsDanh mục liên quan đến Photoelectric Sensors
FAQ Photoelectric Sensors
- Question: What is the range of Detection Distance available for the sensors?
- Answer: The range of photoelectric sensor detection distance available for the sensors depends on the type of photoelectric sensor and the object being detected.
Here are some examples of typical detection distances for different types of photoelectric sensors:
1. Retroreflective photoelectric sensors: Retroreflective photoelectric sensors have a detection distance of up to 30 meters or more.
2. Diffuse photoelectric sensors: Diffuse photoelectric sensors have a detection distance of up to 10 meters or more.
3.Through-beam photoelectric sensors: Through-beam photoelectric sensors have a detection distance of up to 100 meters or more.
However, it is important to note that the detection distance of a photoelectric sensor can be affected by a number of factors, such as the environment, the object being detected, and the sensor's settings. - Question: How do Photoelectric Sensors Work in Various Industrial Applications?
- Answer: Photoelectric sensors are widely employed in various industrial applications to detect objects, monitor processes, and ensure safety. For example,
1. Object Detection: In automation, photoelectric sensors identify the presence or absence of objects on conveyor belts, enabling precise control of material or parts flow.
2. Distance Measurement: By measuring the time it takes for light to bounce back from an object (time-of-flight), these sensors provide distance data for robotics, positioning, or anti-collision systems.
3. Level Sensing: In tanks or hoppers, these sensors monitor fluid or material levels, ensuring timely refills or preventing overflows.
4. Label Detection: In packaging, they verify the presence and alignment of labels, ensuring accurate product labeling.
5. Edge Detection: Photoelectric sensors maintain alignment in printing and paper industries.
6. Counting: They tally products on assembly lines, helping manage inventory and quality control. - Question: What are the Different Types of Photoelectric Sensors and How to Choose the Right One?
- Answer: Photoelectric sensors come in various types, and choosing the right one depends on your specific application. Here are the key types:
1. Through-Beam Sensors: These consist of a separate emitter and receiver, offering high accuracy over long distances. Ideal for precise object detection, such as conveyor systems.
2. Retro-Reflective Sensors: Use a reflector to bounce light back to the sensor. Suited for medium-range applications like door control systems and parking barriers.
3. Diffuse Reflective Sensors: Combine emitter and receiver in one housing. They are versatile for close-range object detection, suitable for packaging and assembly lines.
4. Polarized Sensors: Use polarized light to minimize glare and reflections, making them great for glossy or reflective surfaces, like label detection on shiny packages. - Question: What are the Key Features to Consider When Selecting a Photoelectric Sensor?
- Answer: When selecting a photoelectric sensor, consider the following key features to ensure it suits your application:
1. Type of Sensor: Choose from through-beam, retro-reflective, diffuse reflective, polarized, depending on your specific needs.
2. Detection Range: Ensure the sensor's range covers the distance at which objects need to be detected within your application.
3. Environmental Conditions: Consider factors like temperature, humidity, and the presence of dust or contaminants. Select a sensor designed to withstand the environment it will operate in.
4. Output Type: Determine if the sensor's output (e.g., NPN, PNP, ) is compatible with your control system for seamless integration.
5. Shape and Size: Ensure the sensor's physical dimensions and shape fit within the available space in your application.
6. Object Characteristics: Consider the material, size, color, and surface characteristics of the objects you need to detect, as this can impact sensor performance.
7. Power Supply Compatibility: Ensure the sensor's voltage and power requirements match your machine's power supply. - Question: How to Install and Maintain Photoelectric Sensors for Optimal Performance?
- Answer: Installation:
1. Mounting: Securely mount the sensor in a stable position, ensuring it aligns properly with the objects to be detected.
2. Alignment: Carefully align the emitter and receiver (for through-beam and retro-reflective sensors) to establish a clear line of sight.
3. Protection: Shield sensors from harsh environmental factors using protective enclosures or covers when necessary.
4. Cabling: Use high-quality, shielded cables to minimize interference and ensure reliable connections.
Maintenance:
1. Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the sensor's emitter and receiver to remove dust or dirt that may affect performance.
2. Calibration: Perform routine calibration to maintain accuracy, especially in critical applications.
3. Cable Inspection: Check cable connections for tightness and any signs of wear or damage. Replace damaged cables promptly.
4. Environmental Checks: Monitor the operating environment for changes in temperature, humidity, or other factors that may affect the sensor.
5. Record Keeping: Maintain records of maintenance activities, including cleaning, calibration, and cable replacements.
6. Replacement Schedule: Consider implementing a schedule for periodic sensor replacement, as sensors may degrade over time.























How can we improve?
How can we improve?
While we are not able to respond directly to comments submitted in this form, the information will be reviewed for future improvement.
Customer Privacy Policy
Thank you for your cooperation.
While we are not able to respond directly to comments submitted in this form, the information will be reviewed for future improvement.
Please use the inquiry form.
Customer Privacy Policy